Direcit- Fit Three Way Catalytic Converter
-

Direct Fit Catalytic Converter HYUNDAI 2014-2017 Elantra Exhaust System
Three-way catalysis mainly uses some rare and precious metals to purify and reduce exhaust gases. For example, platinum, rhodium, and palladium are used as catalysts to oxidize and reduce carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides in the exhaust. Carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water are thus produced and discharged.
Its structure is composed of shell, catalyst coating, shock absorbing pad, heat insulation layer and carrier.
There are two types of carriers, metal and rare earth ceramics, which are shaped like honeycombs. Currently, family cars mainly use 400-mesh carriers.
-

High Quality three-way catalytic converter Genesis G80 3.8L V6 catalysts 2017
Generally, the three-way catalytic converter is usually installed at the front end of the exhaust system. Specifically, it is located inside the first bulge of the engine exhaust pipe, with front and rear oxygen sensors respectively. These sensors detect the amount of oxygen in the exhaust and adjust the engine’s air-fuel ratio to ensure the catalyst is working properly.
-

A Catalytic Converter Is Used to 2010-2012 Hyundai Genesis Aftermarket
Quality ensured by extensive testing processes
Delivers leak-free performance
Meets OE specifications for product fit, form and function
Offers superior wear resistance
-

High performance Exhaust Catalytic Converter Fits 2010-2012 Hyundai Genesis
The three-way catalytic converter is a key emission control technology in modern automobiles. It is located at the front end of the automobile’s exhaust system, specifically installed in the first bulge of the engine’s exhaust pipe. In this position, the three-way catalytic converter can work closely with the front and rear oxygen sensors to ensure the normal operation of the engine.
-

Direct Fit 2016 Hyundai Genesis Catalytic Converter Aftermarket
The three-way catalytic converter is the most important external purification device installed in the automobile exhaust system. It can convert harmful gases such as CO, HC and NOx emitted by the automobile exhaust into harmless carbon dioxide, water and NOx through oxidation and reduction. Nitrogen.
-

Auto Parts Catalytic Converter 2012-2016 Hyundai Genesis 6 Cyl 3.8L
The three-way catalytic converter is installed at the head of the car’s exhaust pipe. The three-way catalytic converter is used to purify exhaust gas and reduce toxic and harmful substances in the exhaust gas. Every gasoline car has a three-way catalytic converter. The automobile exhaust pipe consists of three sections, namely the head section, the middle section and the tail section. The front section is directly connected to the engine, the middle section is fixed to the chassis, and the rear section is close to the rear bumper.
-

Auto Parts Three Way Catalytic Converter Geely Aftermarket
It mainly uses some rare and precious metals to purify and reduce exhaust gases, such as platinum, rhodium, and palladium as catalysts to oxidize and reduce carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides in the exhaust. Carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water are thus produced and discharged.
-
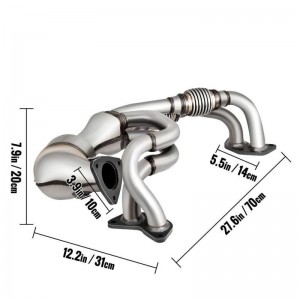
Auto Parts Catalytic Converter fits Subaru Forester Impreza Legacy Outback 2006 – 2010 2.5L
The three-way catalytic converter assembly can meet the long-term use requirements of the conventional operating temperature range of the actual vehicle exhaust system from -40°C to 950°C.
-

Good Quality And Price Of Three-way High Flow Catalytic Converter For Ford Racer 2.0t
When the engine combustion exhaust gas flows through the surface of the honeycomb ceramic carrier and the temperature of the carrier surface reaches a specific temperature range,
The harmful chemical components HC, CO and NOx in the combustion exhaust gas will produce corresponding chemical reactions with the chemical coating on the carrier wall.
-

three way catalytic converter for Volkswagen SKODA
In order to allow the catalytic converter gas flow to have a larger surface circulation area, the carrier is usually made into a honeycomb shape with very thin wall thickness to make full use of the limited space. At present, the main product specifications mostly use 400 mesh (400 holes/square inch) or 600 mesh (600 holes/square inch) ceramic honeycomb carrier. During the extrusion process, a large number of thin-walled, parallel, usually square channels are generated.
-

Ceramic exhaust catalytic converter for Volkswagen For VW Tiguan 1.8T 2.0T
The exhaust gas of gasoline engines contains CO, HC and NOx, which are pollutants. The three-way catalytic converter is an essential part of the exhaust gas purification device of gasoline engines. It can greatly reduce the degree of pollution of the exhaust gas to the atmosphere.
-

Hot Selling Three-Way Catalytic Converter Car Accessory
Three-way catalytic purification technology is also the most important purification method for light vehicle exhaust at present. Its main function is to convert three pollutants in car exhaust – carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides into non-toxic substances. Reduce engine exhaust pollutants


















